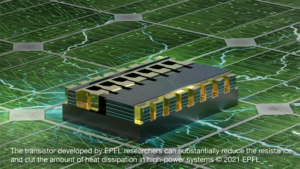
New Transistor Design Reduces Energy Dissipation in High-power Applications
In their paper, the researchers introduce a nanowire-based device to create high-electron-mobility tri-gate transistors for power-conversion applications. Based on nanoscale structures, the novel transistor design significantly reduces heat loss during the energy conversion process.
Can Influencers Sway Public Opinion?
Contrary to expectations, the experiment revealed that the respondents held on to their views firmly, regardless of the celebrity inputs or their esteem in the eyes of the respondents. It was also clear that respondents liked to hear an opinion identical to their own even if it came from a disliked celebrity. Conversely, a dissenting opinion by a celebrity or expert reduced the respondent’s empathy for that person.
EPFL’s PowerSGD Algorithm Features in Software Industry
Two EPFL students have developed PowerSGD, an algorithm that allows compression of the needed bandwidth without compromising the accuracy of the training.